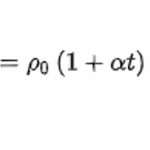Apple released M1 chip upgrade memory, graphics performance significantly improved
Apple Inc. held a new fall conference. At this event, in addition to releasing the new generation of TWS headphones…
TSMC’s U.S. factory to produce 5nm chips for cell phones from 2024, sources say
TSMC’s fab in Phoenix, Arizona, will produce 5nm chips starting in 2024, when the company says it will have a…
Build a chip factory, India also came to join the fun
Recently, the media said that India is discussing with China’s Taiwan-based foundry UMC to build a joint wafer fab matters,…
Embracing the decade of 5G innovation: Huawei unveils 5Gigaverse solution
During the 2021QQ Mobile Broadband Forum, Huawei officially unveiled a full range of innovative solutions for the 5Gigaverse. At a…
Not escaping the supply chain crisis, even Apple is facing a “chip shortage”
QQ market cap ZG Apple Z has not escaped the supply chain crisis, joining a growing number of large companies…
What is the function of the series resistor of the output of the active crystal?
Generally, large companies have minimalist designs for their hardware circuits, which are the result of long-term experience, in order to…
What are the types of resistors? These three types must be understood
Classification by voltammetric characteristics For most conductors, at a certain temperature, their resistance remains almost constant and is a certain…
What is a resistor? What are the parts of a resistor?
A resistor is commonly referred to as a resistor in everyday life. It is a current-limiting element. When a resistor…
What is resistance? What are the factors that affect resistance?
What is resistance? The resistance of a conductor to an electric current is called the resistance of that conductor. Resistor…
How to prevent air holes in PCBA processing soldering?
PCBA board soldering generated porosity, which we often say air bubbles, generally in the PCBA processing process of reflow soldering…